Popüler Motorlar
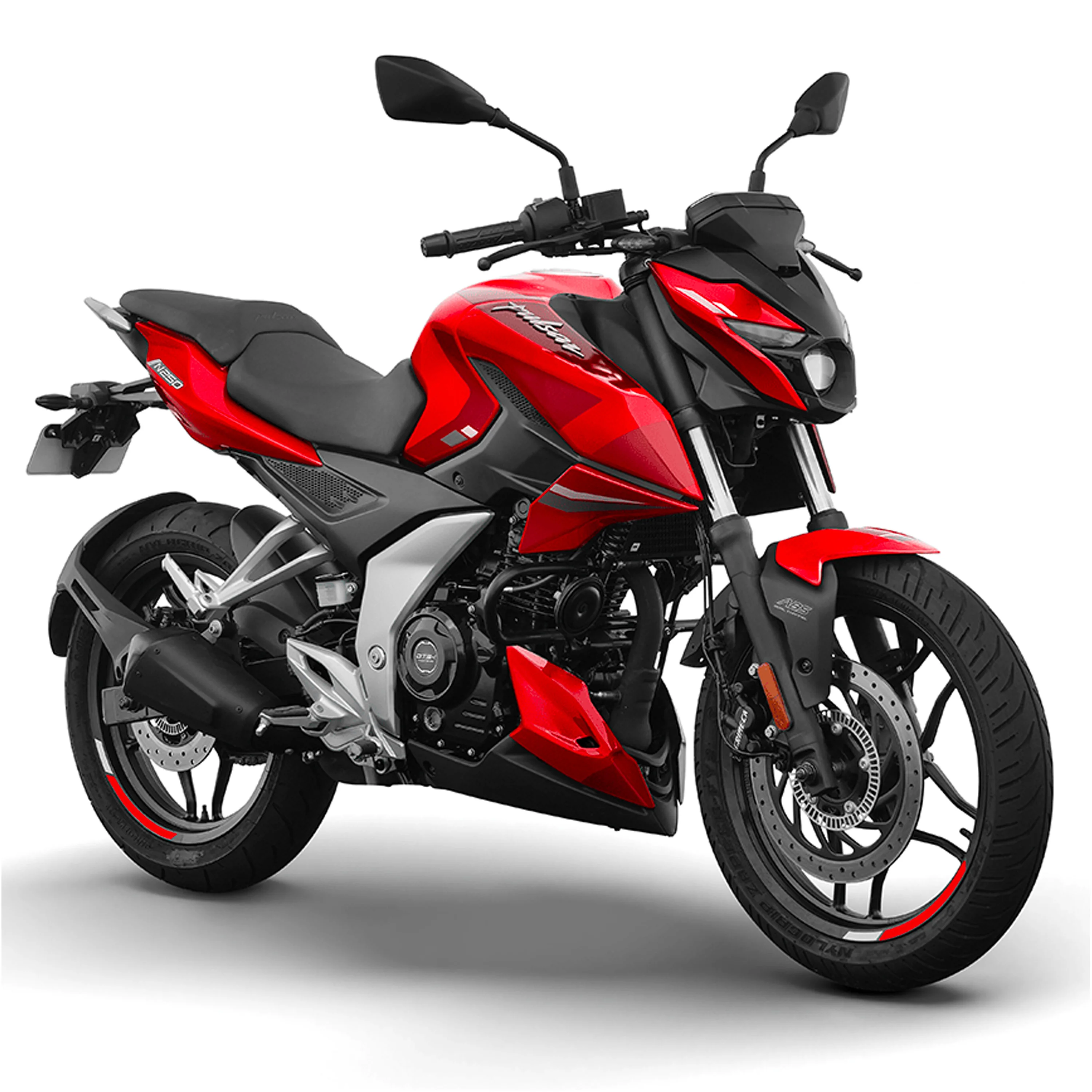

Motor 1
Motor 1 hakkında bilgi.
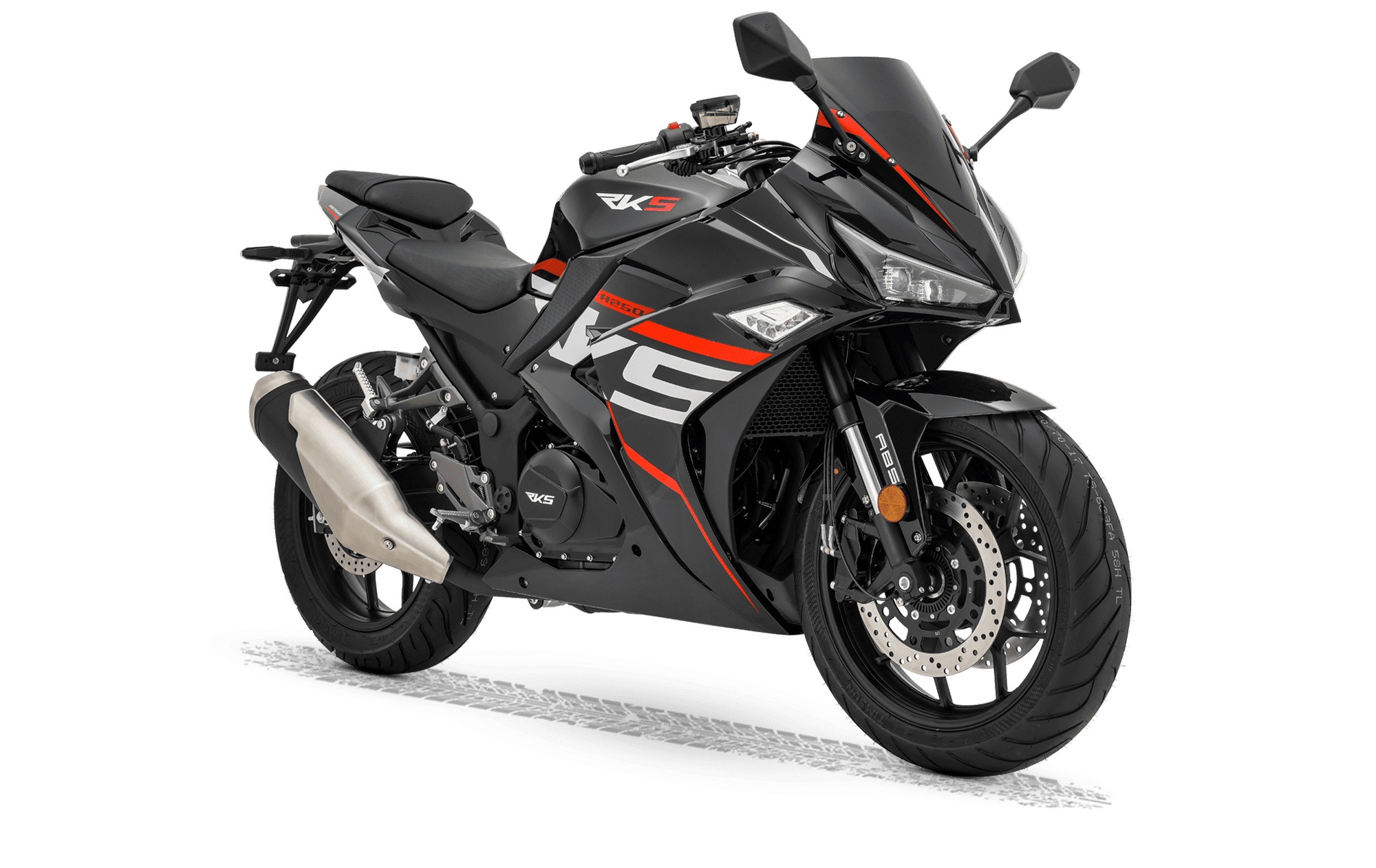
Motor 2
Motor 2 hakkında bilgi.

Motor 3
Motor 3 hakkında bilgi.
Motor tutkunlarına özel platform

Motor 1 hakkında bilgi.

Motor 2 hakkında bilgi.

Motor 3 hakkında bilgi.